MINOCA – The New Unique Type of Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarctions have been claiming lives since ancient times, yet we are still understanding the condition itself. With the emergence of acute coronary angiography in the 80s, it became evident nearly 90% of myocardial infarctions are associated with occluded coronary arteries. This led to the advances in clinical approaches to reduce the myocardial damage by reopening the obstructed coronary arteries as quickly as possible with the aid of mechanical and pharmacological interventions. Among all this, a distinctive form of myocardial infarction have been silently increasing in prevalence over the years without drawing much attention. This subtype of myocardial infarction has recently been named “myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries’ or ‘MINOCA’. As the name implies, it refers to patients presenting with myocardial infarct symptoms without obstructive coronary artery disease. The lack of obstructive coronary artery disease in this group often leads clinicians to disregard them as “false-positive presentations” and patients are discharged with “it doesn’t seem like there is anything wrong with you and there is not much I can do about it at this stage.” Despite a myocardial infarct presentation, patients are discharged to home with minimal to no medical management and no explanation. With the widespread use of coronary angiography and the advance of more sensitive cardiac biomarkers, the MINOCA presentations have started to gain attention among cardiologists and researchers in recent years.
This year at Scientific Sessions 2018, Dr Jacqueline E. Tamis-Holland and Dr Harmony Reynolds addressed MINOCA and the existing knowledge gap. Here is a summary of the key points discussed at the meeting:
What is MINOCA?
Approximately 5-10% of myocardial infarct presentations are suspected as MINOCA and available data suggests that they are likely be younger, females and have lower cardiovascular risk factors than myocardial infarct patients with obstructed arteries. The recent 4th universal definition of myocardial infarction published in 2018 highlighted that the diagnosis of MINOCA indicates that there is an ischemic mechanism responsible for the myocyte injury. Therefore, the MINOCA diagnosis is not applied to patients with clinical evidence of aberrant troponin changes as a result of non-ischemic or non-cardiac causes such as myocarditis or pulmonary embolism.

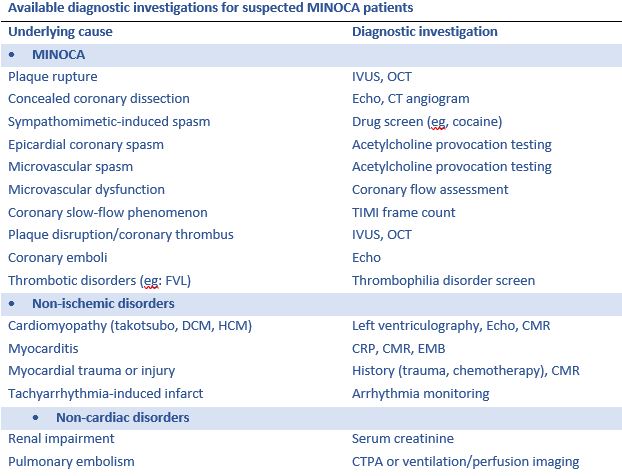
What causes MINOCA and what are the additional recommended tests?
The dilemma with treating MINOCA is delineating MINOCA presentations from those with troponin rise and/or fall due to non-ischemic and non-cardiac causes as this not feasible based on the presentation itself. When a patient is suspected as MINOCA following coronary angiography, the patient should be clinically re-evaluated with multiple potential causes in mind. The following are the key underlying causes and corresponding diagnostic investigations.
Prognosis of MINOCA
The available literature demonstrates that overall suspected MINOCA patients have a favorable prognosis compared to those with the classic myocardial infarction (associated with obstructive CAD). However, careful examination of literature shows suspected MINOCA patients have the equivalent 12-month all-cause mortality to those with myocardial infarction associated with single- or double-vessel coronary artery disease. However, the prognosis associated with MINOCA with only ischemic mechanisms in mind is yet to be studied.
Treatment for MINOCA
There are no randomized trials addressing this question. However, a recent publication by Lindahl and colleagues stemming from the SWEDEHEART (Swedish Web-System for Enhancement and Development of Evidence-Based Care in Heart Disease Evaluated According to Recommended Therapy) registry provides the first insights into potential long-term prognostic benefit of medical therapy in the management of MINOCA. The authors have showed benefits of statins, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers and beta-blocker therapy in MINOCA cohort.
The MINOCA BAT Trial (Randomized Evaluation of β‐Blocker and Angiotensin‐Converting Enzyme Inhibitor/Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Treatment in MINOCA Patients) is the first randomized clinical trial initiative in MINOCA patients and expected to begin enrollment in Australia and Europe in 2018 and also plans to expand enrollment to the United States and Canada in the next year. This will be a pragmatic prospective, randomized, multicentre, open-label clinical trial, with 2×2 factorial design. All outcomes will be analyzed using the intention-to-treat principle. The study aims to determine whether oral beta-blockade and/or ACEI/ARB impacts on MACE in patients discharged with MINOCA, where MACE is defined as the 4-year composite endpoint of all-cause mortality or hospital admission for AMI, ischemic stroke or heart failure.
As evident from Scientific Sessions 2018, the current available MINOCA literature demonstrates the importance of diagnosing and treating patients with MINOCA, although substantial knowledge gaps exist that require future research to identify optimal management.
Key points about MINOCA
- MINOCA is not uncommon occurring in approximately 5-10% of patients.
- MINOCA indicates that there is an ischemic mechanism responsible for the myocyte injury.
- MINOCA diagnosis is not applied to patients with clinical evidence of aberrant troponin changes
- There are various etiologies for MINOCA and it is important to perform a careful evaluation to identify the cause
- Treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause but there may be some role for cardioprotective therapies in MINOCA
- The prognosis of MINOCA is not benign, once again emphasizing proper diagnosis and aggressive treatment for this condition
“The good physician treats the disease; the great physician treats the patient who has the disease” – William Osler
Do you have any thoughts on MINOCA?
