The Significant Areas of Interest in the Field of Cardiac Imaging in 2018
There were several exciting developments in 2018 with regards to cardiac imaging. The role of the cardiac imager is becoming increasingly relevant in today’s cardiology practice environment and bridges across several subspecialties in Cardiology, such as electrophysiology with the use of transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) in the placement of left atrial appendage closure devices. These devices include Watchman and interventional cardiology with structural and valvular heart disease and echocardiographic guidance with transaortic valve replacement (TAVR), percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitralClip, as well as atrial septal and ventricular septal closure devices. The field of cardiac imaging has matured over the years and not only includes echocardiography and nuclear cardiology, but also includes advanced imaging with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI) and cardiac computed tomography. In addition, there has been the rise of the interventional echocardiographer specializing in the use of echocardiography in guiding percutaneous and surgical treatment of structural heart disease. In fact, there has been recognition of cardiac imaging by several professional societies such as the American College of Cardiology with publication of the state-of-the-art paper, The Future of Cardiac Imaging Report of a Think Tank Convened by the American College of Cardiology1. There have also been several disease states that have been positively influenced by the development of new diagnostic technology in cardiac imaging, such as cardiac amyloidosis. Cardiac imaging has also positively influenced preventive cardiology with release of the latest American Heart Association (AHA)/ American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2018 Cholesterol Management Guidelines2. The following areas were, in my opinion, considered topics of great interest in 2018 in the field of cardiac imaging.
Nuclear Imaging
Cardiac Amyloidosis. For several years, cardiac amyloidosis, particularly transthyretin type (ATTR type), was thought to be a diagnosis that was very difficult to make with endomyocardial biopsy being the only method to confirm the diagnosis. However, nuclear cardiac imaging has changed the landscape of this disease with the novel application of old technology with the use of technetium 99m pyrophosphate (Tc-99m PYP) in the diagnosis of ATTR type cardiac amyloidosis3. The sensitivity and specificity of this technique in diagnosing this disease state is >95%, and oftentimes avoids the need for endomyocardial biopsy to make this diagnosis4. The development of this technique in diagnosing the disease has increased the recognition of this disease in many patients with diastolic heart failure, and even in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis undergoing TAVR. This has also led to greater research and development of new treatments for this disease, such as tafamidis, patisiran and inotersen. The development of these medications will hopefully improve the overall prognosis for patients with this disease.
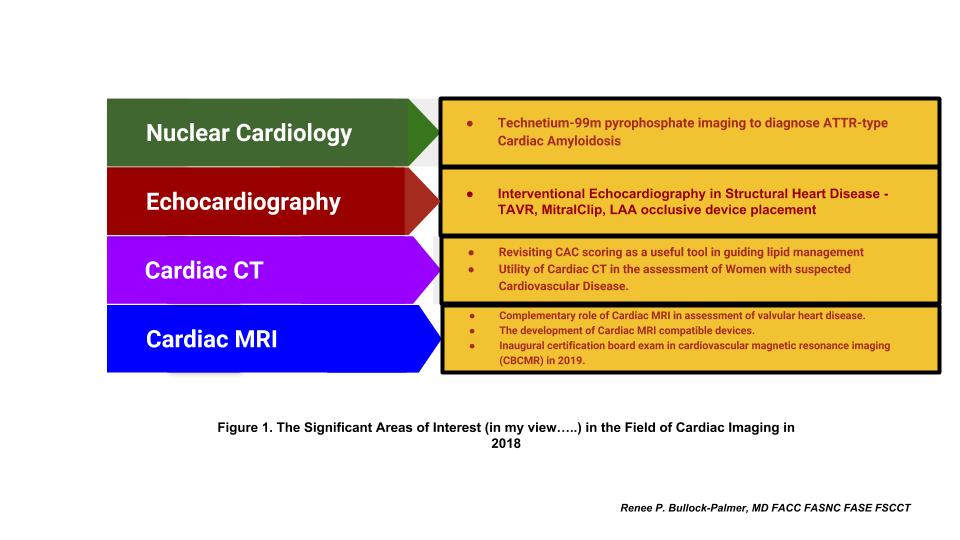
Echocardiography
The Rise of the Interventional Echocardiographer in Structural Cardiac Imaging. There has been increasingly relevant areas of interest in structural heart disease, such as percutaneous mitral valve repair with MitralClip, especially with the release of the study findings from the COAPT trial5. In addition, transaortic valve replacement (TAVR) has become increasingly available for many patients with severe aortic valve stenosis, and many institutions have began offering this therapy to many of their patients. Additionally, left atrial appendage occlusive devices such as the Watchman device are being increasingly used in patients with atrial fibrillation who are at high risk for hemorrhagic complications with anticoagulation, despite having indications for thromboembolic prophylaxis. With these new developments, there has been the rise of the interventional echocardiographer, who serves a vital role with the use of echocardiography in guiding the placement of these devices in the treatment of structural heart disease. Many fellows are now seeking additional training in this field to meet this demand, as this area has invited a growing interest in the cardiology field and has attracted many trainees.
Cardiac Computed Tomography
The revisiting of Coronary Calcium Score as a Powerful Tool in Preventive Cardiology. The release of the latest AHA/ACC Cholesterol Management Guidelines has been an area of great interest in the field. The latest guidelines have included the use of coronary calcium scoring with cardiac CT as a tool to further risk stratify patients to guide the use of pharmacologic therapy for patients with hyperlipidemia2. This has led to the resurgence of Cardiac CT for coronary calcium scoring as a valuable tool for cardiologists in the field of preventive cardiology.
Utility of Cardiac CT in the assessment of Women with suspected Cardiovascular Disease. There has also been the increasing recognition of Cardiac CT as a useful diagnostic tool for women suspected of having cardiovascular disease (CVD)6. Hopefully, this will result in the increased appropriate use of Cardiac CT in the management of CVD in women.
Cardiac MRI
The complementary role of Cardiac MRI with echocardiography and assessment of valvular and structural heart disease. Cardiac MRI has become an established imaging modality in the assessment of valvular heart disease. This has been embraced by the American Society of Echocardiography’s latest Valvular Guidelines, which includes cardiac MRI as playing a complementary role in the assessment of the severity and etiology of valvular heart disease7. The use of Cardiac MRI is also useful in the assessment of other disease states, such hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and risk assessment for sudden death8.
The rise of Cardiac MRI compatible devices. There has also been the development of Cardiac MRI compatible devices which now allows many patients with these devices to be able to have cardiac MRIs performed safely. Cardiac MRI is therefore a viable diagnostic tool for these patients.
The first administration of certification board exam in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CBCMR). With the maturation of Cardiac MRI as a viable imaging modality, 2019 will see the inaugural administration of the first certification exam in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CBCMR), which will occur between May 7 – June 7, 2019, and the 2019 application window will open on January 15, 2019.
Conclusion:
With the dawn of a new year in 2019, it is clear that the future of cardiac imaging is very bright. I am looking forward to many more promising developments in this field and hope that this field will continue to attract many more talented cardiologists in this area of cardiology.
References:
- Douglas PS, Cerqueira MD, Berman DS, Chinnaiyan K, Cohen MS, Lundbye JB, et al. The Future of Cardiac Imaging Report of a Think Tank Convened by the American College of Cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 2016;9:1211–23.
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam LT, Birtcher KK, et al. 2018AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. JACC Nov 2018, 25709; DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.003.
- Dorbala S, Bokhari S, Miller E, Bullock-Palmer RP, Soman P, Thompson R. ASNC Practice Points: 99mTechnetium-Pyrophosphate Imaging for Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis (American Society of Nuclear Cardiology website). 2018. Available at: https://www.asnc.org/Files/Practice%20Resources/Practice%20Points/ASNC%20Practice%20Point-99mTechnetiumPyrophosphateImaging2016.pdf.
- Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, Merlini G, Damy T, Dispenzieri A, et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation. 2016 Jun 14;133(24):2404-12. Doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021612. Epub 2016 Apr 22.
- Stone GW, Lindenfeld J, Abraham WT, Kar S, Lim DS, Mishell JM,et al. COAPT Investigators.Transcatheter Mitral-Valve Repair in Patients with Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 13;379(24):2307-2318. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806640. Epub 2018 Sep 23.
- Truong QA, Rinehart S, Abbara S, Achenbach S, Berman DS, Bullock-Palmer R,et al. SCCT Women’s Committee.Coronary computed tomographic imaging in women: An expert consensus statement from the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2018 Nov – Dec;12(6):451-466. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2018.10.019. Epub 2018 Oct 23.
- Zoghbi WA, Adams D, Bonow RO, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, et al. Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017 Apr;30(4):303-371. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Mar 14.
- Weng Z, Yao J, Chan RH, He J, Yang X, Zhou Y, He Y.Prognostic Value of LGE-CMR in HCM: A Meta-Analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Dec;9(12):1392-1402. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.02.031. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Review.







 Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the number one cause of mortality for both men and women in the United States1. Although CVD related mortality is decreasing with advanced diagnostic testing and therapies of CVD, the prevalence of this disease remains high including in the younger aged population younger than 55 years of age1. This suggests that as providers we have done a successful job at treating CVD however there remains a lot of work to be done with regards to preventing this disease.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the number one cause of mortality for both men and women in the United States1. Although CVD related mortality is decreasing with advanced diagnostic testing and therapies of CVD, the prevalence of this disease remains high including in the younger aged population younger than 55 years of age1. This suggests that as providers we have done a successful job at treating CVD however there remains a lot of work to be done with regards to preventing this disease.